DNA
DNA is the acronym for Deoxy Ribonucleic acid, and it’s the molecule found in the nucleus inside a human cell. Its primary function is to store and encode the genetic data of the body. In the majority of the cycle of a cell the DNA is contained within the cell’s nucleus like a coiled noodles. But when cells reproduce the DNA, it is placed in the form of structures called chromosomes. They help to maintain the stability of DNA during the process that cells replicate. The majority of us are acquainted with the dual helix model of DNA. You’ve probably seen it in movies, films or even in books. Double helix models illustrates that DNA is an organic polymer. In order to comprehend DNA’s structure in a more clear manner it is essential to know the definition of polymers.
DNA As A Polymer
The polymer is essentially a molecule that is composed of many repeating units, which are referred to as monomers. Consider, for instance an ordinary polymer such as starch. In this case the monomeric units that are repeating are referred to as glucose. The glucose molecules are joined by glycosidic bonding and create the polymer called starch. Similar to DNA, it is also a non-polymer and when it comes to DNA the monomeric units which make up it are referred to as nucleotides. The fundamental shape of a nucleotide follows as follows.
Like you see it is composed of three groups that are important – sugar, phosphate and an nitrogenous base. The sugar contained in the nucleotide is known as Deoxyribose it is a 5-carbon sugar which is part of the pentoses. The phosphate group is comprised of a phosphorus ion in which 4 oxygen molecules have been attached. In addition, we have nitrogenous bases. They comprise organic compounds that include nitrogen and are formed as rings.
There are four types of bases that may be found within DNA molecules. They include Adenine, Guanine, Cytosine and Thymine. There are four different kinds of nitrogenous bases There are four distinct kinds of nucleotides in the DNA structure..
What is DNA and How Does it Work?
The four nucleotides are placed within two distinct groups. One group, referred to as pyrimidines. They include base nitrogenous thymine and cytosine. They have both been identified as single-ringed base. The second group is comprised of nucleotides, also commonly referred to as purines. They contain adenine and guanine as nitrogenous bases. Both are double-ringed.
Form follows function. This was the principle of the architect Louis Henry Sullivan. It demonstrates how the two are interconnected and not separate. The idea posed by the architect can be applied to any kind of design, whether industrial or print, web or even a product.
Many designers aren’t aware of this truth. In reality, we’ve seen many designs that lack shape or unusable. The truth is that even corporate websites are frequently equally guilty as other websites. It’s obvious but it’s crucial to know what they are doing wrong and how they can make changes.
Many of the major corporate websites are filled with job opportunities because they’re full of details. The problem is that they lack an attractive design. However small personal websites are usually striking. There are galleries, bios portfolios, stories, and portfolios but they’re not fully functional. These kinds of websites do not have a lot to do with marketing because they rarely sell anything.
The Structure and Function of DNA
The structure is quite simple for starch. It is made up of long long chains of glucose connected by glycosidic bonds. However, in DNA, the four kinds of nucleotides are joined in a highly complex manner to create the double the helix. We can now look at the model of the double helix structure of DNA.
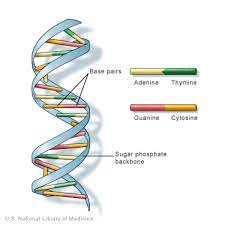
It is clear the basic structure of two blue lines wrapped around each other. There are also lines in the middle connecting the blue lines. To better understand the model when we unravel the model, we’ll discover something commonly referred to as the model for step ladders of DNA.
It shares a similar shape and is comprised of blue vertical lines, as well as other lines which connect them. These blue vertical lines symbolize the sugar-phosphate core of DNA, while the lines in the middle are the base pairs of the DNA.
How Are Two Nucleotides Joined Together?
The DNA’s cards that are contained within the deoxyribose sugar in DNA are numbered between 1 and 5 in the counterclockwise direction. The third carbon of every deoxyribose glucose forms a bonds with the group of phosphate in another nucleotide beneath it. The bonding now extends both ways. The phosphates are linked to two sugars, one bond is with the carbon 3 of sugar above and another that is the fifth carbon sugar below. Due to the bonds formed between sugar and phosphates there’s a type of sugar-phosphate backbone that is formed on the other side. It is basically the DNA of a single strand.
This helps us understand the way that the nucleotides of the DNA strand are linked to form the sugar-phosphate backbone, which is represented in the blue line that are visible in the structure. The lines that are in the middle are the base pairs of one side. On the other hand there is the second DNA strand which could be very similar to the first one, but with some crucial distinctions. To comprehend these differences, it is necessary to understand the concepts of directionality as well as the concept of complementary base pairing.
Definition of DNA
The chemical orientation from end to end for a single line nucleic acid is referred to as directionality. The direction of DNA can be described in two ways: 5 3′ to 5 or 3 5′ to 3′. If we examine the DNA’s strand it is possible to find the 5′ end where the phosphate group is attached as well as the 3′ end to where a hydroxyl group is connected. If we look back at the DNA strand that was originally stranded, we will observe that it is running in 5′ to 3 direction. The opposite strand is also similar but has one significant differentiator that it runs in an entirely opposite direction, which is 3′-5′. This indicates that DNA’s two DNA strands are oppositely parallel.
The rule of thumb is that there can be no form without a purpose and there can be no function without a function. The key to success is the balance. A balance that is strong between both form and purpose is the key to realize the concept of perfection. Function must be understood prior to the design is designed.
Finding work isn’t as simple. There are many websites that lack purpose and are not functional. Know your market, understand your products and services and how you’ll perform your job in order to do this, you’ll be able to create your own set of tasks.
Medical Definition of DNA
To build a model take a look at how you feel of the site’s structure, its purpose, the organization expectations, structure, and functions before you make your very own model. What color is best suited to the website? Do you require lots of images or text? Are they accessible enough to navigate effortlessly? Finding the answer to these questions will provide you with an idea of the type of form you need to fill out.
The balance is extremely difficult to identify and utilize, but the web isn’t yet mature enough to warrant exploring and testing. No matter how difficult it may be for us, it is imperative to find the right balance to achieve our ultimate aim.
This is the way in the various nitrogenous bases in DNA molecules match up with each the other. In essence, the base Adenine pairs with Thymine as well as The base Guanine always joins Cytosine. As you can see in the above step-ladder diagram The base A is paired with the base T while the C base is paired to the G base. The bases are responsible for making hydrogen bonds that are in the middle which binds the two strands of DNA to each other. The importance of pairing bases with complementary bases is since it helps maintain the right spacing between two of the strands that comprise DNA. This is crucial to ensure the stability of both DNA strands.
Conclusion
This is the entire story of DNA’s fundamental structure and functions. We hope you find it useful. If you are interested in learning more about DNA as well as its components, go to the online website for education and you’ll get what you’re looking for.
According to the Carry Harrow



