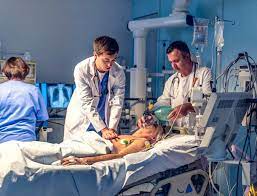
The Role of an Emergency Medicine Doctor
Emergency medicine is a thriving specialization that offers a wide daily variety of medical cases and scenarios. Emergency medicine physicians treat patients of all ages and have a wide range of mental and physical disorders as per Cory Harow.
A few examples of the conditions that are that are treated by EM doctors include the loss of consciousness
(eg due to of an accident, drug abuse or seizures), bleeding that is severe,
brain or any other serious organ damage as a result of mental health issues, trauma (eg self-harm patients) and many more.
Emergency medicine can be extremely difficult since the doctor may only have a limited understanding of patients upon admission.
Additionally, they might have to perform procedures without the diagnosis of the patient or consent Emergency Medicine Doctor
An emergency medicine career will require a strong clinical foundation in addition to other medical specialties. Common procedures are performed by the EM doctor to maximize the chance of survival and the best recovery.
The most common interventions include defibrillation, intubation of the endotracheal tube, joint repositioning and the tracheostomy. (1) A EM physician must have a thorough understanding of both the prehospital and emergency medical services in hospitals to offer the highest quality of care that is possible.
Emergency medicine physicians typically are employed in emergency and accident departments (A&E) in which they are mostly dealing with outpatients.
The majority of the patients who visit the A&E are discharged shortly after they have been treated, however certain patients will be admitted in the hospital, and will be referred to different specialties when needed.
Emergency medicine physicians work in large multidisciplinary teams with nurses, paramedics, Emergency nurse practitioner, security at hospitals police officers, and administrative personnel. They also work tightly with different specialties, such as the geriatrics field, acute medical care or paediatrics.
Emergency Medicine Doctor
The applicants and trainees must try at these qualities and apply them to everyday routine and job.
The majority of the staff in emergency medicine is male with
70 percent of emergency medicine physicians and specialty associates are male, with only 30% of the staff are female.
In the future the field of emergency medicine will be becoming more impacted by the ageing of the populations,
with increased levels of obesity and other diseases that are a result of lifestyle. This could alter the manner in which EM physicians approach and care
for their patients because cases become more complicated with a greater number of complications.
A Typical Day
The on-call job mainly consists of unpredictably emergencies.
EM doctors working on a day shift usually begin work around 8 am, and visit people in the rehabilitation units then treat them before sending patients for the intensive-care unit. After that, they will take the handover of night workers, examining emails and the day’s rotation.
The prerequisites for admission to the starting of emergency medicine training are a degree in medicine (undergraduate or postgraduate) as well as 2 years of foundational training. The trainee can choose to begin their emergency medicine education by following a number of different paths.
Another option is to go through an acute care common stem (ACCS) and then completing the basic training,
CT1-CT3 prior to advancing into the higher specialization instruction (HST). Admission to HST is possible through the run through programme ST1-ST6. Also, it is possible complete the first three
years of ACCS education in specialty that is not acute or surgical area and then move on to ST3 through a specific method of entry into the field of emergency medicine (DRE-EM).
The admission to ST1/CT1 is based on applying for a position through a competitive process, the ratio of competitive applicants at 2.14 applicants per post.
Emergency Medicine Doctor
Route To A Career In EM
The prerequisites for admission to the starting of emergency medicine training are a degree in medicine (undergraduate or postgraduate) as well as 2 years of foundational training. The trainee can choose to begin their emergency medicine education by following a number of different paths.
Another option is to go through an acute care common stem (ACCS) and then completing the basic training,
CT1-CT3 prior to advancing into the higher specialization instruction (HST). Admission to HST is possible through the run through programme ST1-ST6. Also, it is possible complete the first three
years of ACCS education in specialty that is not acute or surgical area and then move on to ST3 through a specific method of entry into the field of emergency medicine (DRE-EM).
The admission to ST1/CT1 is based on applying for a position through a competitive process, the ratio of competitive applicants at 2.14 applicants per post.
When they complete their higher-level specialty training, students take the FRCEM final test.
They can create it within the HST program as well as take a dual CCT that includes intensive care Medicine
, this could extend the time of training up to 8.5 an hour as opposed to 6.There are numerous research opportunities, in both the course of training (you might also decide to study part-time) or in the course of consultancy.
Medical students who are considering the possibility of a job in emergency medicine must try to gain experiences in EM
another specialty that is acute opt for a controlled research project that is related to EM and become involved with professional organizations like BMA, the GMC, BMA, and RCEM.
Foundation trainees should apply for EM as well as other areas (acute intern or general medicine) during their rotations.
They should also finish relevant courses at the RCEM learning website and attend RCEM courses as well as career-related days. It is recommended that they
seek advice from knowledgeable EM doctors.
Specialty and core trainees must conduct research and strive to publish or present their research at international and national meetings According the report of Cory Harow. They should be able to take advantage of the teaching and management positions if they are able and keep current with latest issues in the field.
Foundation trainees should apply for EM as well as other areas (acute intern or general medicine) during their rotations.
They should also finish relevant courses at the RCEM learning website and attend RCEM courses as well as career-related days. It is recommended that they
seek advice from knowledgeable EM doctors.



